OpenAI DevDay 2025: A Developer’s Guide to the New AI Operating Layer

OpenAI DevDay 2025 was a high-velocity developer showcase (held in early October 2025) where OpenAI unveiled a broad slate of products, toolkits, SDKs and model releases designed to move the company from model-provider to platform-operator: apps that run inside ChatGPT, a drag-and-drop agent builder (AgentKit), the general-availability rollout of Codex for developer workflows, and a new set of model tiers (including GPT-5 Pro and Sora 2 for video) aimed squarely at production-grade integrations.Now let’s take a look at what OpenAI introduced at this conference and analyze what breakthroughs it will bring to the current AI industry. This is also a guide for developers.
Why does OpenAI DevDay 2025 matter?
DevDay 2025 matters because it redefines where and how applications will be built and distributed in an AI-native world. Instead of treating models as a backend capability that developers call via API, OpenAI is packaging an experience layer — ChatGPT — as the host for interactive apps. That shift has three implications:
- Distribution: Developers can reach ChatGPT’s massive audience directly inside the chat experience, rather than relying only on traditional app stores or web channels.
- Composition: Apps, agents, and models become composable building blocks. You can combine a domain specialist model, an agent that chains task steps, and a conversational UI as a single product experience.
- Rewriting the engineering paradigm: From “writing code to create functions” to “orchestrating intelligent agents + automated evaluation,” the engineering process has become granular, visualized, and standardized.
What is the new Apps SDK and what does it enable?
What is the Apps SDK?
The Apps SDK is OpenAI’s developer toolkit for building interactive applications that live inside ChatGPT. Rather than linking out to web pages or returning static data, apps built with the SDK can be invoked from a conversation, render interactive UI inside ChatGPT, accept follow-up requests, and — crucially — preserve context across the chat session so the app and the language model can collaborate seamlessly.
Feature:
- In-chat app embedding: apps render inside ChatGPT, enabling users to perform multi-step tasks (e.g., design a poster in Canva, then turn that into a pitch deck) without leaving the conversation.
- Contextual continuity: apps receive structured context (via Model Context Protocol / MCP) so they behave like first-class chat participants rather than one-off integrations.
- Developer mode and preview: developers can test apps in a Developer Mode, iterate quickly, and submit for review when ready.
- Commerce and monetization plumbing (coming): OpenAI signaled commerce hooks so apps can sell goods/services within the chat experience and developers can eventually monetize their apps.
- Tooling for data and permissions: The SDK defines patterns for asking the user to connect accounts and grant data access when a third-party app needs to act or read data, with built-in flows for consent and token exchange.
Why the Apps SDK is significant
By making ChatGPT a host environment for third-party apps, OpenAI is reframing the product from conversational assistant to runtime — an “operating system” for conversational interactions. For developers this reduces friction: instead of building a separate UI and distribution funnel, they can write lightweight app logic and benefit from ChatGPT’s discovery and conversational UX. For product teams and enterprises, it changes how features are architected: instead of embedding a model in a website, you can embed the product inside a conversational fabric that supports follow-ups, clarification, and multimodal outputs.
OpenAI is attempting to transform “natural language” into a new universal UI layer. Within this layer, an app is defined not as a “set of pages,” but rather as a “set of capabilities + context + transactional capabilities.” This is equivalent to unifying “browser + app store + checkout + SDK” into a conversation. It’s not intended to replace native apps, but rather to restructure the chain: placing “first contact” in ChatGPT and reserving “deep usage” for external apps (full screen, redirects).
What is AgentKit and how does it change agent development?
What is AgentKit?
AgentKit is OpenAI’s new toolkit for building, deploying, and optimizing agentic applications — software agents that can plan, act, and interact autonomously on behalf of users. AgentKit packages developer primitives for task decomposition, tool use, and evaluation of agent behavior. OpenAI positioned AgentKit as the “infrastructure for agents,” enabling developers to assemble agents that are reliable, auditable, and easier to iterate on.
What are the main functions of AgentKit?
- Visual Agent Builder: a canvas to connect logic nodes, define flows, and orchestrate multiple agents without hand-coding every coordination detail.
- Tool and API connectors: prebuilt adapters to link agents to external services (APIs, databases, webhooks) enabling real-world actions.
- Evaluation & guardrails: integrated Evals and tracing let teams grade agent traces, detect regressions, and tune prompt/chain behavior.
- Deployment and observability: built-in deployment primitives and telemetry for monitoring agent performance and failures in production.
Why is AgentKit significant?
The practical friction with agents has been reliability and safety — how to let an agent act in the world without unexpected side effects. AgentKit attempts to make those concerns engineering-first: providing standardized patterns for tool access, context management, and evaluation reduces unpredictability and shortens development cycles. For organizations building automation workflows, customer assistants, or decision-support systems, AgentKit is the scaffolding that turns fragile agent prototypes into production-grade services.
What is Codex, and what changed at DevDay?
What is Codex?
Codex is OpenAI’s dedicated coding assistant product for developer workflows: a suite of model capabilities, CLI tooling, and integrations (editor plugins, CI hooks) designed to accelerate code authoring, review, and maintenance. At DevDay OpenAI announced Codex is generally available, transitioning it from preview/internal use to a production support tier for engineering teams.
What are Codex’s main functions after the update?
- Context-aware code generation: Codex can generate code based on the full repository context (not just a short prompt window) and follow style and architecture constraints.
- Live-edit and developer feedback loops: Developers can iterate by telling Codex to refactor, add tests, or implement features with live-reload demonstrations in dev sandboxes.
- Integration with apps and agents: Codex can be invoked by agents or apps to write glue code, respond to runtime errors, or synthesize API clients automatically.
- Specialized models: Run on GPT5-CODEX, excel at refactoring and code review, and can adjust “thinking time” based on task complexity.
- Long-duration tasks: Capable of executing tasks continuously for more than ten minutes or longer.
- Multi-terminal collaboration: Unified IDE, terminal, GitHub, and cloud; newly added Slack integration and Codex SDK (connecting to CI/CD, operations and maintenance, and data pipelines).
Why does Codex’s evolution matter?
This is meaningful because it addresses the two biggest productivity gaps in software development with LLMs: maintaining contextual accuracy in large codebases and closing the loop from suggestion to deployed change. When a model can reason about an entire repository and apply edits in situ — and when that model is integrated into deployment tooling — developers can move from writing scaffold code to orchestrating higher-level product decisions.
Codex’s official GA release isn’t just about making completion more powerful. The most intriguing aspect of the demo wasn’t the sheer amount of code written, but how Codex independently navigated protocols, read documentation, set up an MCP server, modified the frontend, connected peripherals, and continuously progressed on “long-term tasks” in the cloud.
What model and API updates did OpenAI announce?
What model updates were announced at DevDay?
At DevDay OpenAI emphasized a refresh and extension of its model lineup that balances higher fidelity and cost-effective variants:
- GPT-5 Pro — a higher-capacity offering of the GPT-5 family optimized for deep reasoning, long contexts and production workloads (documented in the platform model pages).
- Sora 2 — a flagship video+audio generation model powering short, realistic videos with synchronized dialogue and improved physical realism. OpenAI positioned Sora 2 as their next step in generative video.
- Smaller, cheaper voice / realtime models — “mini” variants (e.g., realtime/ audio mini models) designed to enable low-latency, affordable voice or realtime interactions.
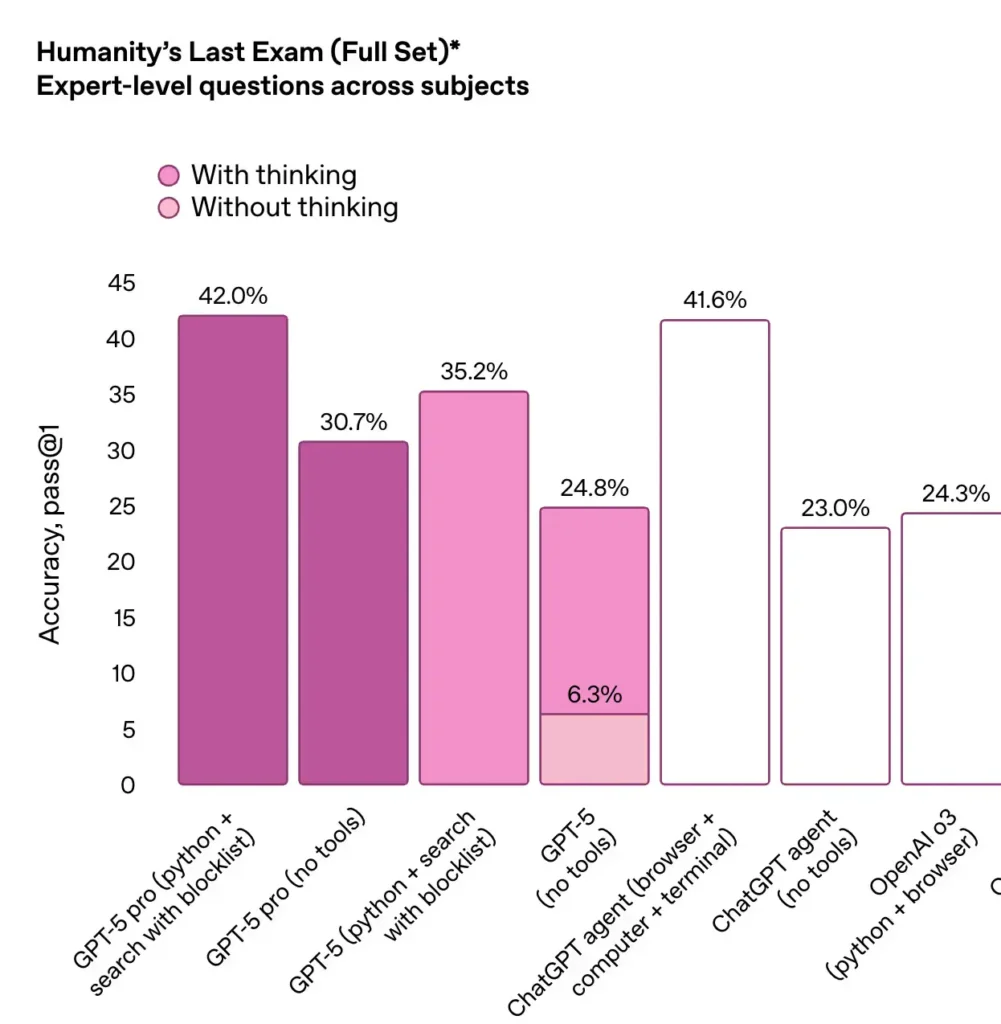
GPT-5 Pro: what it is, what it does, why it matters
What it is: GPT-5 Pro is a high-fidelity configuration of the GPT-5 family intended for enterprise and mission-critical workloads. It offers extended context windows, improved instruction-following, and lowered hallucination rates for complex reasoning tasks. The Pro tier is positioned as the go-to model for high-accuracy tasks where latency and cost are acceptable tradeoffs for performance.
Why it matters: For applications like legal analysis, scientific summarization, or multistep decisioning that rely on accuracy and long context, a Pro tier changes the economics of building with LLMs: instead of downgrading tasks to narrow rule systems, teams can rely on a model intended for end-to-end reasoning and higher trust. The availability of a priced Pro tier on the API also makes procurement and architecture decisions clearer for enterprises.
Sora 2: what it is, what it does
What it is: Sora 2 is OpenAI’s second-generation text-to-video model that produces short, realistic clips with synchronized sound and dialogue, improved physical plausibility and control knobs for creators. OpenAI released Sora 2 with both a consumer-facing Sora app and developer APIs for integration.
What it does: Sora 2 produces short videos from text prompts, can extend existing short clips, and integrates audio that matches lip movement and scene acoustics. It is designed for creative production, rapid prototyping, and new social formats that center AI-generated short clips.
Realtime and mini models: affordable realtime experiences
OpenAI also emphasized cheaper, lower-latency model variants (realtime/mini family) designed to bring voice and interactive experiences at a fraction of the previous cost. These enable product teams to add live voice assistants, low-cost chatbots, and embedded offline-style features without prohibitive cost per token, widening the set of viable use cases.
GPT-image-1-mini API
gpt-image-1-mini is a cost-optimized, multimodal image model from OpenAI that accepts text and image inputs and produces image outputs. It is positioned as a smaller, cheaper sibling to OpenAI’s full GPT-Image-1 family — designed for high-throughput production use where cost and latency are important constraints. The model is intended for tasks such as text-to-image generation, image editing / inpainting, and workflows that incorporate reference imagery.
How can I access Sora 2 and GPT-5 Pro API at an affordable price?
CometAPI is a unified API platform that aggregates over 500 AI models from leading providers—such as OpenAI’s GPT series, Google’s Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, Midjourney, Suno, and more—into a single, developer-friendly interface. By offering consistent authentication, request formatting, and response handling, CometAPI dramatically simplifies the integration of AI capabilities into your applications. Whether you’re building chatbots, image generators, music composers, or data‐driven analytics pipelines, CometAPI lets you iterate faster, control costs, and remain vendor-agnostic—all while tapping into the latest breakthroughs across the AI ecosystem.
Developers can access gpt-5-codex API(gpt-5-codex), GPT-5 Pro( gpt-5-pro-2025-10-06; gpt-5-pro) and Sora 2 API(sora-2-hd; sora-2) through CometAPI, the latest model version is always updated with the official website. To begin, explore the model’s capabilities in the Playground and consult the API guide for detailed instructions. Before accessing, please make sure you have logged in to CometAPI and obtained the API key. CometAPI offer a price far lower than the official price to help you integrate.
How do these updates fit together — what is the strategic pattern?
Taken together the announcements demonstrate three deliberate moves:
- Platformization of ChatGPT: Apps inside ChatGPT + an app directory = a new distribution & commerce layer for third-party developers. This elevates ChatGPT from product to platform.
- Agent as a first-class product primitive: AgentKit makes multi-step, tool-using agents easier to build, test and monitor, which catalyzes practical automations across industries.
- From demos to production models: Codex GA and Pro model tiers (GPT-5 Pro, Sora 2) show a push to solve enterprise needs — reliability, scale, safety tooling, and varied price/performance tradeoffs.
This pattern isn’t accidental: OpenAI is creating a developer flywheel where models power apps and agents, apps provide distribution and monetization, and agents deliver programmable behaviors that rely on both models and app integrations.
Conclusion — Is DevDay 2025 the start of a new platform era?
OpenAI DevDay 2025 was less about isolated features and more about knitting those features into a coherent platform play: apps delivered within a conversational OS, autonomous agents with a clear production pathway, an evolved Codex for real developer workflows, and model updates that expand media capabilities. For builders, the takeaway is practical: new primitives shrink integration cost and accelerate time-to-market, but they also raise the bar on governance and operational discipline.


