How to Access and Use the GPT-5-Codex-Mini

OpenAI recently announced several updates, including the release of the GPT-5-Codex-Mini model, improvements to the rate limit for multi-user hierarchies, and optimizations to model processing efficiency.
OpenAI’s GPT-5-Codex-Mini is a newly announced, developer-focused variant of GPT-5-Codex: a smaller, cost-and-throughput-optimized model intended to deliver most of the coding assistance of GPT-5-Codex but at much lower cost and higher usable volume. The “Mini” variant is positioned as a pragmatic choice for long coding sessions, background automation, and high-frequency developer workflows where raw peak capability is less important than getting more tokens/requests for the same plan.
What is GPT-5-Codex-Mini and its feature?
GPT-5-Codex-Mini is a compact, cost-efficient variant of OpenAI’s GPT-5-Codex family specifically packaged for the Codex product surfaces (CLI and IDE integration). It’s positioned as a “smaller, more cost-efficient” model that trades a small amount of peak capability for materially lower resource consumption and higher usable quota for interactive developer workflows. The mini model is intended to let developers run many more coding turns (OpenAI describes roughly 4× more usage for the same ChatGPT subscription tier) while keeping latency and costs down for common, well-defined engineering tasks.
In terms of capabilities, GPT-5-Codex-Mini inherits the core features of the Codex product line: a deep understanding of the codebase and the execution of multi-step tasks in an “agent” manner. Based on the Codex CLI features, developers can submit natural language commands, code snippets, screenshots, or interface design diagrams to Codex in an interactive terminal. The model will first provide a plan, and then automatically browse files, edit code, run commands, and test after obtaining user approval.
From a modal perspective, Codex products allow attaching images (such as UI screenshots, design drafts, or error message screenshots) to the session in the terminal or IDE. The model can understand both text and image content, but the output is still mainly text code and explanations. Therefore, GPT-5-Codex-Mini can be considered as a code proxy model that is mainly “text + image input, text output”, and does not undertake tasks such as image generation, audio generation or video generation.
How does GPT-5-Codex-Mini compare to GPT-5-Codex?
What’s new in Codex?
In addition to the GPT-5-Codex-Mini realsed, OpenAI has uniformly increased the Codex rate limit by 50% for ChatGPT Plus, Business, and Edu user levels, significantly increasing the available request limit. Meanwhile, ChatGPT Pro users will gain priority processing permissions to improve response speed and task execution experience.
Furthermore, OpenAI has made a minor upgrade to the GPT-5-Codex model, optimizing its performance in collaborative scenarios. The updated model shows improvements of several percentage points on key evaluation metrics, an approximately 3% increase in token usage efficiency, and greater robustness in handling edge cases, thereby reducing the need for user guidance.
| user level | GPT-5-Codex | GPT-5-Codex-Mini |
|---|---|---|
| Plus/Biz/Edu | increases message volume by 1.5xrespectively. | increases message volume by 6x respectively. |
GPT-5-Codex-Mini vs GPT-5-Codex:benchmarks differences
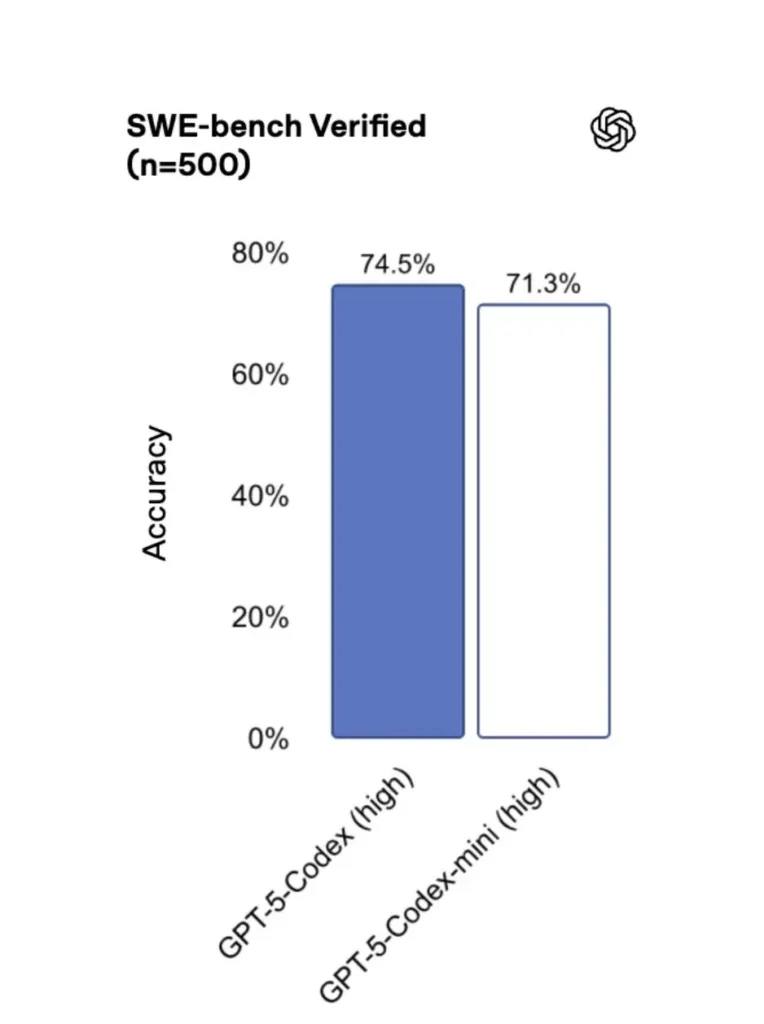
GPT-5-Codex-Mini compared to the original version, its performance is slightly reduced, but developers receive approximately four times the usage credit. In the SWE-bench Verified test, GPT-5 High scored 72.8%, GPT-5-Codex scored 74.5%, and GPT-5-Codex-Mini scored 71.3%.
Codex (and its mini variant) use dramatically fewer tokens for lightweight interactions—OpenAI’s materials claim reductions on the order of tens of percentage points for simple prompts (e.g., a cited figure of ≈93.7% fewer tokens on lightweight interactions for the Codex family vs. GPT-5 in some scenarios).
GPT-5-Codex-Mini vs GPT-5-Codex:feature differences
- Size & cost: Mini is explicitly smaller and more cost-efficient; OpenAI frames it as enabling about 4× more usage under the same subscription constraints. This is a quota/efficiency optimization for routine developer tasks.
- Capability envelope: GPT-5-Codex remains the higher-capability option for long, complex agentic tasks (large refactors, deep code reviews, extended test cycles). Mini is tuned to be snappier and less resource-intensive for frequent short interactions.
- Latency and rate limits: Mini typically delivers lower latency and allows higher rate limits per plan — making it suitable for dense, interactive workflows.
- Default surfaces: Mini is available as a selectable model in Codex CLI and the IDE Extension; GPT-5-Codex is the default for cloud tasks and deep code review flows in Codex.
When to use Mini vs. Full Codex
- Use Mini for: scaffolding, repetitive code generation, small refactors, interactive completions during editing, and when working under a quota or cost constraint.
- Use GPT-5-Codex for: comprehensive code reviews, multi-hour autonomous tasks, complex refactors, and tasks requiring the model’s strongest reasoning and test-driven execution.
How can I access GPT-5-Codex-Mini (CLI, IDE, API)?
Codex CLI (terminal-first)
OpenAI introduced gpt-5-codex-mini as a model option inside the Codex CLI. Typical usage patterns follow the Codex CLI workflow: start an interactive session, specify the model, attach files or screenshots, run “Codex Cloud tasks,” and more. The CLI also supports quick /model switching between full gpt-5-codex and gpt-5-codex-mini. Upon first run, you will need to authenticate using your ChatGPT/Pro/Enterprise account (or provide an API key). The CLI provides various commands that enable Codex to scan codebases, run tests, open REPLs, or apply patch recommendations.
Example (Codex CLI interactive session):
# Install Codex CLI (npm)
npm i -g @openai/codex
# or Homebrew on macOS
brew install --cask codex
# Launch in a repo
cd myproject
# Open a codex interactive session
codex
# In the session you can switch the model:
# (this is typed in the Codex TUI)
> /model gpt-5-codex-mini
# Ask Codex to generate a unit test
> Write pytest tests for function `calculate_discount` in discounts.pyThat flow mirrors the new Codex CLI defaults where the tool will suggest Mini near usage limits.
VS Code / IDE Extension
Yes — the Codex IDE extension (VS Code) already includes gpt-5-codex-mini as an option. Install the Codex extension in Visual Studio Code to get inline code completion, refactoring suggestions, and AI-driven quick fixes. The extension also exposes quick actions (generate code, explain selected code, refactor) and can run Codex Cloud tasks from the editor, VS Code steps:
- Install the OpenAI Codex / ChatGPT extension for VS Code.
- Sign in with your ChatGPT account (Plus/Pro/Business).
- Open the command palette:
Cmd/Ctrl+Shift+P → Codex: Set Model→ choosegpt-5-codex-mini. - Use inline commands (select code → right-click → “Explain with Codex” or press configured hotkey).
Example: VS Code inline command (pseudo steps)
- Select a function in
user_service.py. - Press
Cmd/Ctrl+Shift+P → Codex: Explain Selectionor use the right-click → “Explain with Codex.” - The extension opens a side panel with Mini’s explanation, suggested tests, and a one-click “Create PR” button that uses Codex Cloud tasks to push a branch for review.
How about the API — can I call it from my app?
OpenAI’s announcements indicate API support is coming soon for GPT-5-Codex-Mini; at time of writing the model is available in the Codex toolchain first (CLI/IDE). This means production API clients should prepare for the model name gpt-5-codex-mini in the Requests/Responses API once it’s published. In the meantime, you can prototype with the Codex CLI and IDE flows.
When API access is enabled, a typical call (Responses-style) might look like:
# illustrative — check OpenAI docs for final param names
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(api_key="sk-...")
resp = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-codex-mini",
input="Write a Python function that validates an email address and includes unit tests.",
max_tokens=512,
temperature=0.2
)
print(resp.output_text)
What are best practices for rapid engineering with Codex Mini?
Below are concrete, field-tested best practices and patterns to get maximal value from Codex Mini in production engineering workflows.
1) Model selection strategy — mix and match
Use Mini for high-frequency, lower-complexity tasks (formatting, small refactors, auto tests), and fall back to full Codex for complex design, deep debugging, or large repo-wide transformations. Automate the switch: the Codex CLI already suggests Mini at 90% usage, and you can script /model switching in your tooling to choose a model based on task complexity.
2) Prompt engineering templates
Craft small, deterministic prompt templates for repeatable tasks: test generation, changelog drafts, commit message generation, and PR descriptions. Store these as reusable snippets in your repo or as Codex prompt presets.
Example prompt template for unit tests:
# Template: generate_pytests
System: You are a precise Python developer. Produce pytest tests.
User: Given the function below, produce parametrized pytest functions that cover typical edge cases.
--- file: discounts.py
<insert function>
---
Return only valid Python test code with imports and fixtures.
3) Automate safety nets — approvals & CI gating
Never allow a model to directly push code without human approval. Use Codex’s approval modes and Codex Cloud tasks to create diffs and require human sign-off in CI. The Codex CLI supports “approval modes” so edits must be approved before being applied.
4) Cache and deduplicate model calls
For repetitive prompts (e.g., explaining a function), cache the response keyed by prompt + file hash. This reduces redundant calls and keeps the cost profile predictable.
5) Use streaming + incremental diffs
When possible, request streaming outputs and incremental diffs rather than whole-file rewrites. This lowers token use and helps reviewers see targeted changes.
6) Unit test-first generator flow
Generate tests and run them locally in an ephemeral environment. If tests fail, iterate with the model supplying failing-test fixes. Frame each iteration as a discrete prompt with the test outputs included.
Example Codex CLI automation snippet (bash):
# Generate tests
codex --model gpt-5-codex-mini request "Generate pytest tests for discounts.py" > generated_tests.py
# Run tests locally
pytest generated_tests.py -q || {
echo "Tests failed. Opening Codex for debugging..."
codex --model gpt-5-codex-mini request "Tests failed. Here's pytest output: $(tail -n 50 pytest_output.txt). Propose a fix for discounts.py."
}Conclusion
GPT-5-Codex-Mini is a pragmatic product move: it acknowledges that developer workflows are often dominated by many short interactions where latency, cost, and uninterrupted flow matter. By providing a mini tier aimed at IDE and CLI usage, OpenAI gives teams the ability to scale day-to-day coding assistance without immediately invoking the highest-cost model for every interaction.
CometAPI promises to keep track of the latest model dynamics including GPT-5-Codex-Min API, which will be released simultaneously with the official release. Please look forward to it and continue to pay attention to CometAPI. While waiting, you can pay attention to other models, explore the model’s capabilities in the Playground and consult the API guide for detailed instructions. Developers can access GPT-5-Codex API ,GPT-5 Pro API through CometAPI, the cometAPI’s latest models listed are as of the article’s publication date. Before accessing, please make sure you have logged in to CometAPI and obtained the API key.CometAPI offer a price far lower than the official price to help you integrate.
Ready to Go?→ Sign up for CometAPI today !
If you want to know more tips, guides and news on AI follow us on VK, X and Discord!


