What is Qwen?
Qwen (Tongyi Qianwen) is a series of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal models developed by Alibaba Cloud, initially launched in beta version in April 2023. By July 2024, it was ranked as a top Chinese language model in certain benchmarks and third globally, only behind leading models from Anthropic and OpenAI. The name “Tongyi Qianwen” translates to “Truth from a Thousand Questions,” reflecting its capability to provide accurate responses across various queries.
This series is built on multilingual data, with a particular emphasis on Chinese and English, but also supports other languages such as Spanish, French, and Japanese. The models range from 1.8 billion parameters (1.8B) to 72 billion parameters (72B), suitable for a wide range of applications from research to enterprise. The series has evolved to include version 2 (launched in June 2024) and version 2.5 (updated in early 2025), introducing innovations like mixture of experts (MoE) architectures and real-time multimodal processing.

How Has Qwen’s Open-Source Policy Evolved Over Time?
Alibaba’s approach to open-sourcing its models has been dynamic, reflecting a balance between fostering collaboration and maintaining competitive advantages. In December 2023, Alibaba open-sourced its 72B and 1.8B models, followed by the 7B model in August of the same year. These early releases were significant, providing researchers and developers with access to powerful AI models under specific licensing agreements.
With the launch of version 2 in June 2024, Alibaba shifted its strategy, keeping its most advanced models proprietary while selectively open-sourcing others. This trend continued with the 2.5 series, where models like 2.5-VL-32B-Instruct (released March 2025) and 2.5-Omni-7B (released March 2025) were made available under the Apache 2.0 license, while 2.5-Max remained closed source. This mixed approach has sparked discussions about the trade-offs between open access and proprietary control in the AI industry.
What Drives Alibaba’s Mixed Strategy?
Alibaba’s open-source policy appears driven by several factors:
- Community Engagement: Open-sourcing models like Qwen2.5-Omni-7B encourages developers to build applications and contribute to the ecosystem, as seen with its availability on platforms like Hugging Face and GitHub.
- Competitive Edge: Keeping advanced models like Qwen2.5-Max proprietary allows Alibaba to maintain a technological lead and monetize through cloud services.
- Regulatory Considerations: Operating in China, Alibaba must navigate government regulations, which may influence its licensing decisions.
This strategy aligns with industry trends, where companies like OpenAI and Meta AI also balance open and closed models to drive innovation while protecting commercial interests.
Which Specific Qwen Models Are Open Source?
The Qwen family encompasses a range of models, with varying open-source statuses. Below is a detailed overview of key models and their licensing:
| Model | Open Source | License | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Instruct | Yes | Apache 2.0 | Hugging Face, ModelScope, GitHub |
| Qwen2.5-Omni-7B | Yes | Apache 2.0 | Hugging Face, ModelScope, GitHub, Qwen Chat |
| Qwen-72B, Qwen-14B, Qwen-7B | Yes | Tongyi Qianwen LICENSE AGREEMENT (commercial use requires application) | Hugging Face, ModelScope |
| Qwen-1.8B | Yes | Tongyi Qianwen RESEARCH LICENSE AGREEMENT (commercial use requires contact) | Hugging Face, ModelScope |
| Qwen2.5-Max | No | Proprietary (API access only) | Qwen Chat, Alibaba Cloud Model Studio |
- Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Instruct: Released in March 2025, this vision-language model excels at processing images and text. It is open source under the Apache 2.0 license, making it freely available for use and modification .
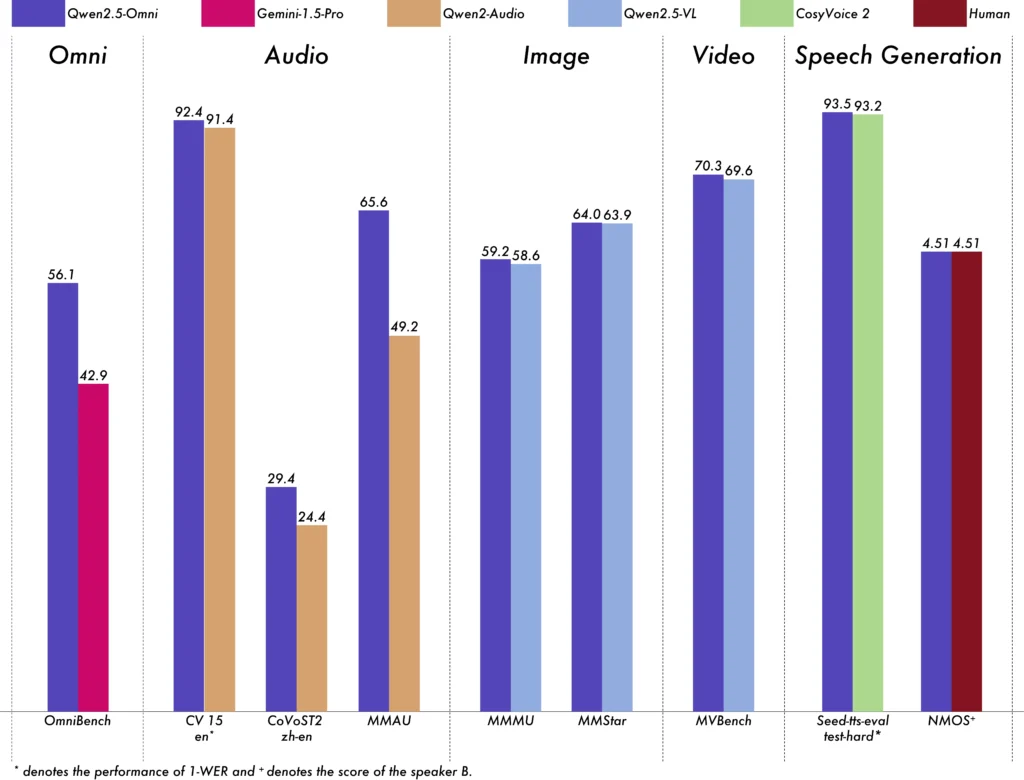
- Qwen2.5-Omni-7B: Launched in March 2025, this multimodal model handles text, images, audio, and video, and is deployable on edge devices like mobile phones. It is also open source under Apache 2.0.
- Qwen-72B, Qwen-14B, Qwen-7B: These earlier models are available under the Tongyi Qianwen LICENSE AGREEMENT, which allows research use but requires an application for commercial purposes.
- Qwen-1.8B: Licensed under the Tongyi Qianwen RESEARCH LICENSE AGREEMENT, this model is primarily for research, with commercial use requiring direct contact with Alibaba.
- Qwen2.5-Max: This model, trained on 20 trillion tokens, is not open source, with its weights kept proprietary. It is accessible only through APIs like Qwen Chat.
The source code for Qwen is generally available under the Apache 2.0 license on GitHub, enabling developers to modify and build upon it, subject to the terms of the license .
How Do Open-Source Models Benefit Developers?
Open-source Qwen models offer several advantages:
- Customization: Developers can fine-tune models for specific applications, as seen with “Liberated Qwen” by Abacus AI .
- Cost-Effectiveness: Free access reduces barriers for startups and researchers, enabling experimentation without significant investment.
- Transparency: Open-source models allow for independent audits, enhancing trust in their performance and ethical use.
However, proprietary models like Qwen2.5-Max limit such flexibility, requiring developers to rely on Alibaba’s infrastructure.

Is Qwen2.5-Max Open Source?
Qwen2.5-Max, a flagship model in the Qwen family, is not open source. Its weights are not publicly available, meaning developers cannot download or modify the model directly. Instead, access is provided through APIs, such as Qwen Chat and Alibaba Cloud’s Model Studio. Launched in January 2025, Qwen2.5-Max outperforms competitors like GPT-4o, DeepSeek-V3, and Llama-3.1-405B in several benchmarks, making it a powerful but restricted tool).
Why Keep Qwen2.5-Max Proprietary?
Alibaba’s decision to keep Qwen2.5-Max proprietary likely stems from:
- Market Positioning: Retaining control over advanced models ensures Alibaba’s competitive edge in the AI market.
- Revenue Generation: APIs and cloud services provide a monetization pathway, supporting further R&D.
- Usage Oversight: Proprietary models allow Alibaba to enforce ethical and legal guidelines, particularly in regulated markets like China.
This approach mirrors strategies by companies like OpenAI, which restricts access to its most advanced models while offering API-based solutions.
How Does Qwen Compare to Other Open Source Models?
Qwen’s open-source models contribute to the growing ecosystem of open-source AI models, including Meta’s Llama (partially based on which Qwen is) and models from Hugging Face. Qwen’s uniqueness lies in its strong multilingual capabilities, particularly in the Chinese domain, less common among Western-developed models.
Additionally, the MoE architecture used in Qwen 2 and later versions represents a frontier approach to model scale and efficiency, attracting interest from the research community. Here is a brief comparison of Qwen with other open-source models:
| Model | Developer | Multilingual Capability | Architectural Innovation | Level of Openness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen | Alibaba Cloud | Strong (Chinese focus) | MoE (Qwen 2+) | Partially open |
| Llama | Meta AI | Medium | Traditional Transformer | Open for research |
| Hugging Face | Community-driven | Diverse | Various | Broadly open |
What Does the Future Hold for Qwen’s Open-Source Policy?
As of April 2025, Alibaba is preparing to release Qwen 3, an upgraded version of its flagship AI model, potentially later this month . While the open-source status of Qwen 3 remains unclear, Alibaba’s recent actions suggest a continued mixed approach. The release of Qwen2.5-Omni-7B in March 2025 under Apache 2.0 indicates a commitment to open-source contributions .
Additionally, a strategic partnership between Manus AI and the Qwen team in March 2025 signals a collaborative approach, potentially leading to more open-source initiatives. This partnership aims to develop advanced AI agents, which could benefit from open-source models to accelerate adoption.
Conclusion:
Qwen is not completely open source, but a mix of open and proprietary. Models like Qwen-72B, Qwen-1.8B, Qwen 7B, and parts of Qwen 2 and Qwen 2.5 are open-sourced under licenses such as Apache 2.0, providing significant resources to the AI community. However, certain advanced models remain proprietary, reflecting Alibaba’s balance between openness and commercial interests.
This strategy allows Qwen to foster widespread adoption and innovation while maintaining Alibaba’s competitive position in the AI field. As Qwen continues to develop, its open-sourcing strategy will remain a key topic of discussion within the AI community.
For Developers: API Access
CometAPI offers a price far lower than the official price to help you integrate Qwen API , and you will get $1 in your account after registering and logging in! Welcome to register and experience CometAPI.
CometAPI acts as a centralized hub for APIs of several leading AI models, eliminating the need to engage with multiple API providers separately.
Please refer to Qwen 2.5 Max API for integration details.CometAPI has updated the latest QwQ-32B API.
