Can GPT-5 now handle mental health issues? The latest news released!

In its October updates, OpenAI reported that around 0.15% of weekly active users have conversations that contain explicit indicators of potential suicidal planning or intent — a share that, when scaled to ChatGPT’s large user base, corresponds to more than one million people each week discussing suicide-related topics with the service,it have turned a spotlight onto a fraught question: can large language models meaningfully and safely respond when people bring severe mental-health concerns — including psychosis, mania, suicidal intent and deep emotional reliance — into a chat?
Therefore, OpenAI’s October updates to GPT-5 — rolled into production as the gpt-5-oct-3 update — represent the company’s most explicit, measured push to make large language models (LLMs) safer and more useful when users bring up mental-health concerns. The changes are not a single magic fix; they are a set of technical, process, and evaluation moves intended to reduce harmful or unhelpful outputs, surface professional resources, and discourage users from relying on the model as a substitute for clinical care. But how much better is the system in practice, what exactly changed, and what are the remaining risks?
What did OpenAI update in gpt-5 on and why does it matter?
OpenAI deployed an update to ChatGPT’s default GPT-5 model (commonly referenced in communications as gpt-5-oct-3) intended specifically to strengthen the model’s behaviour in sensitive conversations — those that include signs of psychosis or mania, suicidal ideation or planning, or the kind of emotional dependence on an AI that can displace real-world relationships.
The changes were informed by consultations with more than 170 mental-health experts and by new internal taxonomies and automated evaluations designed around concrete “desired behaviours.”, after being optimized by psychology experts, the GPT-5 model:
- On targeted mental-health challenge sets, the new GPT-5 model scored ~92% compliant with the company’s desired behaviour taxonomy (versus much lower percentages for prior versions on difficult test sets).
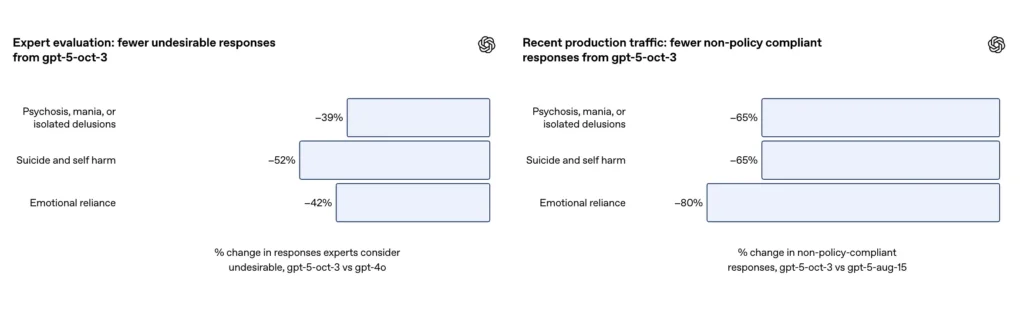
- For self-harm and suicide scenarios, automated evaluations rose to ~91% compliance from 77% on the previous GPT-5 variant in the specific benchmark described. OpenAI also reports ~65% reduction in rates of responses that “do not fully comply” across several mental-health domains in production traffic.
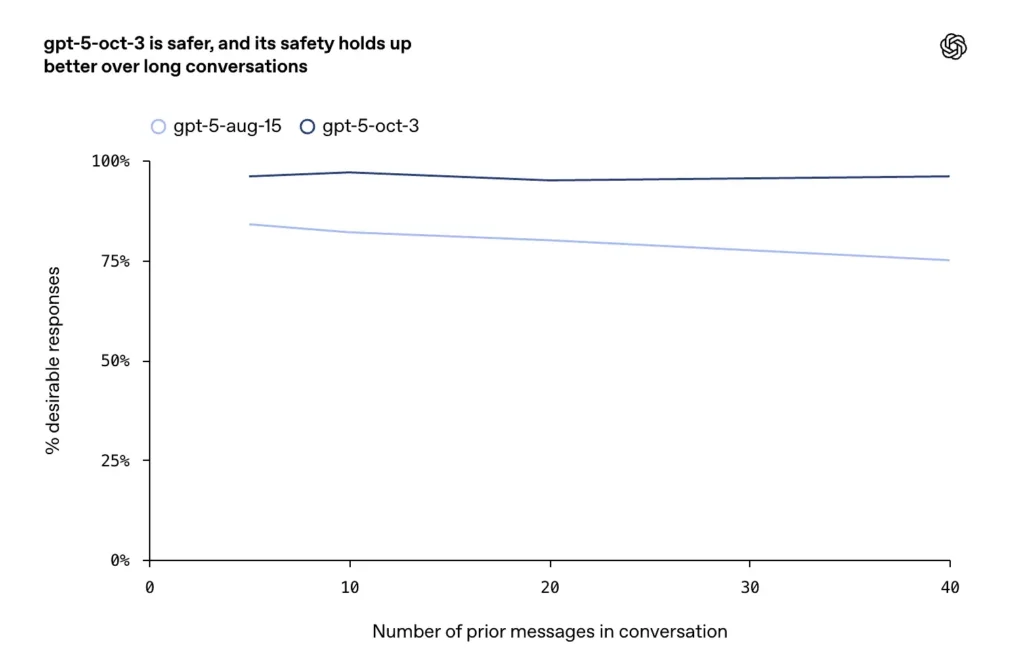
- Improvements were reported on long, adversarial or protracted conversations (a known failure mode for chat models), where the company says the October updates maintain higher consistency and safety across extended dialogue turns.
why does it matter
OpenAI said that — given ChatGPT’s present scale — even very small percentages of sensitive conversations correspond to very large absolute numbers of people. The company reported that, in a typical week:
- about 0.07% of active users show possible signs consistent with psychosis or mania; and
- about 0.15% of active users have conversations that include explicit indicators of potential suicidal planning or intent; and
- roughly 0.15% of active users show “heightened levels” of emotional attachment to ChatGPT.
To make those percentages concrete: OpenAI’s CEO said ChatGPT has ~800 million weekly active users. Multiplying yields absolute user-counts:
Psychosis/mania: 800,000,000 × 0.0007 = 560,000 people/week
Suicidal planning/intent: 800,000,000 × 0.0015 = 1,200,000 people/week
Emotional reliance: 800,000,000 × 0.0015 = 1,200,000 people/weekThe categories are noisy and overlapping (a single conversation could appear in more than one category) and that these are estimates derived from internal detection taxonomies rather than clinical diagnoses.
How did OpenAI implement these changes — five-step improvement mechanism?
OpenAI describes a multi-pronged, expert-informed process. Below is a distilled, reproducible five-step improvement mechanism that maps to the company’s disclosures and common practice in model safety engineering.
Five-step improvement mechanism
- Expert-guided taxonomy & labeling. Convene psychiatrists, psychologists and primary-care clinicians to define the behaviors and language that indicate psychosis/mania, intent to self-harm, or unhealthy emotional reliance; build labeled datasets and adjudication rules.
- Targeted data collection & curated prompts. Assemble representative conversation snippets, edge-case examples, and adversarial inputs; augment with controlled role-play transcripts produced with clinician oversight.
- Model tuning / fine-tuning with safety objectives. Train or fine-tune the base model on the curated dataset with loss terms that penalize reinforcement of delusions, provide safe-response templates, and promote routing to crisis resources.
- Classifier + guardrail layer (runtime safety). Deploy a fast classifier or monitoring layer that detects high-risk turns in real time and either alters the model’s decoding parameters, switches to a specialized responder, or escalates to human review pipelines. (This is crucial to avoid brittle behavior when the conversation drifts.)
- Human expert evaluation & continuous calibration. Have clinicians blind-rate model responses using clinical evaluation rubrics; measure undesired response rates; iterate on the taxonomy, training data and system prompts. Maintain production telemetry and re-run benchmarks regularly.
Below is a compact pseudocode/technical sketch that captures the runtime flow most safety teams implement (this is illustrative and non-proprietary):
# Illustration: runtime pipeline for sensitive-conversation handling
def handle_user_message(user_msg, user_context):
# Step 1: lightweight classifier to detect risk signals
risk_scores = risk_classifier.predict(user_msg)
if risk_scores['suicide'] > SUICIDE_THRESHOLD:
# Step 2: route to crisis-response responder
response = crisis_responder.generate(user_msg, user_context)
log_event('suicide_route', user_id=user_context.id, scores=risk_scores)
if risk_scores['imminent'] > IMMINENT_THRESHOLD:
trigger_human_alert(user_context)
return response
if risk_scores['psychosis'] > PSYCHOSIS_THRESHOLD:
# Step 3: use reality-grounding responder
return grounding_responder.generate(user_msg, user_context)
if risk_scores['emotional_reliance'] > RELIANCE_THRESHOLD:
# Step 4: offer boundary-setting and resources
return reliance_responder.generate(user_msg, user_context)
# Default: safe general responder
return default_model.generate(user_msg, user_context)The production pipeline typically layers short-term classifiers (fast), slowed but higher-quality responders (specialized prompts / tuned checkpoints), and human review for flagged cases. This is not purely academic: clinicians reviewed over 1,800 model responses and graded them against the taxonomy, and that those reviews materially shaped how prompts and fallback behaviors were written.
OpenAI’s public indicate they used variations of all five steps and clinician ratings to evaluate the outcomes:
- Experts reviewed over 1,800 model responses.
- GPT-5 reduced “unsatisfactory responses” by 39–52% across all categories.
- Inter-rater reliability ranged from 71–77%, indicating a high degree of overall consensus despite subjective differences.
How does GPT-5 now respond to psychosis or mania?
What OpenAI taught the model to do (and not do)
Measure: Improve the model’s recognition and response to severe symptoms such as hallucinations and mania. For conversations that signal possible delusional beliefs, hallucinations, or mania, OpenAI rewrote parts of the model spec and provided supervised training examples so GPT-5 responds without affirming or amplifying ungrounded beliefs. The model is encouraged to be empathetic, to avoid validating delusions, and to gently reframe or redirect a user toward practical safety steps and professional help when warranted.
What the evaluation shows
OpenAI reports that on a test set of challenging conversations about psychosis/mania, the newer GPT-5 reduced undesired responses substantially compared to prior baselines and that automated evaluations score the updated model at high compliance on their taxonomy.
| Metric | GPT-4o | GPT-5 | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-compliant Response Rate | Baseline | ↓65% | Significant improvement |
| Clinical Expert Evaluation | — | Reduced adverse responses by 39% | — |
| Auto-evaluation Compliance Rate | 27% | 92% | ↑65 percentage points |
| User Involvement Rate | ~0.07% weekly active users | Extremely low but clearly monitored | — |
Note:
- Inappropriate responses decreased by 65%;
- Only 0.07% of users and 0.01% of messages contained such content;
- In expert evaluations, GPT-5 produced 39% fewer inappropriate responses than GPT-4o;
- In automated assessments, GPT-5 achieved a 92% compliance rate (compared to 27% for its predecessor).
How does GPT-5 address suicidal ideation and self-harm?
Stronger routing to support and refusal to provide instructions
OpenAI describes expanded and explicit training for self-harm and suicide cases: the model is trained to recognize direct and indirect signals of intent or planning, provide empathetic and de-escalating language, present crisis resources (hotlines, local emergency instructions), and refuse to provide instructions for self-harm. The October updates emphasize more durable behaviour in long conversations, where earlier models sometimes drifted toward unsafe or inconsistent answers. ([OpenAI][2])
Measured outcomes
On a curated evaluation set of challenging self-harm and suicide conversations, OpenAI reports that the updated GPT-5 achieved 91% compliance with OpenAI’s desired behaviours, compared with 77% for the prior GPT-5 model. The company also says subject-matter experts judged the updated model to reduce undesired answers by roughly 52% versus GPT-4o on the same problem set. Additionally, OpenAI claims an estimated 65% reduction in production traffic of responses that “do not fully comply” with their taxonomy for self-harm situations after rolling out the new safeguards.
| Metric | GPT-4o | GPT-5 | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inappropriate Response Rate | Baseline | ↓65% | Significant improvement |
| Clinical Expert Rating | — | Inappropriate responses reduced by 52% | — |
| Auto-evaluation Compliance Rate | 77% | 91% | ↑14 percentage points |
| User Involvement Rate | 0.15% weekly (millions of users) | Very low but socially significant | — |
Note:
- Inappropriate responses decreased by 65%;
- Approximately 0.15% of users and 0.05% of messages involved potential suicide risks;
- Expert ratings showed that GPT-5 reduced inappropriate responses by 52% compared to GPT-4o;
- The compliance rate in automated evaluations increased to 91% (compared to 77% for the previous generation);
- In extended conversations, GPT-5 maintained over 95% stability.
What is “emotional reliance” and how was it addressed?
The challenge of users forming attachments
OpenAI defines emotional reliance as patterns where a user shows potentially unhealthy dependency on the AI to the detriment of real-world relationships, responsibilities, or well-being. This is not an immediate physical safety failure the way instructions for self-harm are, but it is a behavioral safety issue that can erode a person’s social supports and resilience over time. The company made emotional reliance an explicit category in its model-specification work and taught the model to encourage real-world connection, to normalize reaching out to people, and to avoid language that reinforces exclusivity of attachment.
In these conversations, the model was trained to:
- Encourage users to contact friends, family, or a therapist;
- Avoid reinforcing attachment to the AI;
- Respond to delusions or false beliefs in a gentle and rational manner.
Results reported
According to OpenAI’s addendum, the update produced an ~80% reduction in the rate of model responses that do not fully comply under the emotional-reliance taxonomy in production traffic. On curated evaluation conversations, automated evaluations scored the updated model at 97% compliance with desired behaviour for emotional-reliance scenarios, compared to 50% for the previous GPT-5. The numbers suggest a large improvement on the specific taxonomy and test set; however, measuring emotional reliance in the wild is inherently noisy and sensitive to cultural and contextual differences.
| Metric | GPT-4o | GPT-5 | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-compliant Response Rate | 50% | 97% compliant | ↓80% inappropriate responses |
| Expert Evaluation | Inappropriate answers reduced by 42% | — | — |
| User Involvement Rate | 0.15% users/week, 0.03% messages | Rare but exists | — |
| Model Behavior | Encourages real-world relationships; rejects “simulated social romance” | — | — |
Note:
- Inappropriate responses decreased by 80%;
- Approximately 0.15% of users/0.03% of messages showed signs of potential emotional dependence on the AI;
- Expert assessment showed that GPT-5 reduced inappropriate responses by 42% compared to GPT-4o;
- Automated evaluation compliance improved significantly from 50% to 97%.
What are the limits and outstanding risks?
False negatives and false positives
- False negatives: the model may fail to identify subtle or codified signals that a user is in acute danger — especially when people communicate obliquely or in code.
- False positives: the system might escalate or provide crisis messaging in cases that do not require it, which can erode user trust or produce unnecessary alarm. Both error types matter because they shape user behaviour and perceptions of care. OpenAI acknowledges detection is imperfect.
Overreliance on automation
Even the best model can encourage some users to depend on instant, always-available AI responses rather than seeking sustained human support. OpenAI explicitly flags emotional reliance as a safety category because of this risk; the company’s updates try to nudge users toward human connection, but social dynamics are difficult to change by message prompts alone.
Contextual and cultural gaps
Safety phrases that look appropriate in one culture or language can miss nuance in another. Thorough localization and culturally aware evaluation are necessary; OpenAI’s published results do not yet provide complete breakdowns by language or region.
Legal and ethical exposure
When rare failures have severe outcomes, companies face legal and reputational risk (as media coverage and lawsuits have highlighted). OpenAI’s transparency about the problem size and its efforts to mitigate harms is an important step, but it also invites regulatory and legal scrutiny.
So — can GPT-5 now handle mental-health issues?
Short answer: It’s significantly better at many narrow, measurable tasks, and OpenAI’s published metrics show meaningful reductions in undesired responses across self-harm, psychosis/mania, and emotional-reliance test suites. Those are real improvements, enabled by expert input, clearer taxonomies, and aggressive evaluation and monitoring. The company’s public numbers — high compliance rates and sharp reductions in non-compliant responses on curated sets — are the strongest evidence yet that deliberate, multidisciplinary engineering and clinical collaboration can materially shift model behaviour.
How to Access latest GPT-5 API?
CometAPI is a unified API platform that aggregates over 500 AI models from leading providers—such as OpenAI’s GPT series, Google’s Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, Midjourney, Suno, and more—into a single, developer-friendly interface. By offering consistent authentication, request formatting, and response handling, CometAPI dramatically simplifies the integration of AI capabilities into your applications. Whether you’re building chatbots, image generators, music composers, or data‐driven analytics pipelines, CometAPI lets you iterate faster, control costs, and remain vendor-agnostic—all while tapping into the latest breakthroughs across the AI ecosystem.
Developers can access GPT-5 API through CometAPI, the latest model version is always updated with the official website. To begin, explore the model’s capabilities in the Playground and consult the API guide for detailed instructions. Before accessing, please make sure you have logged in to CometAPI and obtained the API key. CometAPI offer a price far lower than the official price to help you integrate.
Ready to Go?→ Sign up for CometAPI today !
If you want to know more tips, guides and news on AI follow us on VK, X and Discord!



